Health Check Page 예제
JSP / JAVA
https://github.com/worldline/healthcheck/blob/master/healthcheck/healthcheck-servlet/src/test/java/net/atos/xa/healthcheck/servlet/RegisterHealthCheckTestCase.java
출처 : http://docs.rightscale.com/faq/How_Do_I_Set_Up_a_Health_Check_Page_for_HAProxy.html
Background
This document explains how to create a health-check page that HAProxy will use to check the status of a web server or application.
While the exact contents of your health-check page are not important, its name should be unique (e.g. including a random number). The same page is used for all application servers to determine whether the server is running (up). While you are not prevented from using index.html as the health-check page, this is not recommended. This is because most web sites have an index.html page and, thus, there is a risk that your load balancer will direct client traffic to a web site other than your own in the cloud. For this reason, you should always use a health-check URI with a unique file name.
Example: The Amazon EC2 cloud recycles IP addresses; so, if one server was terminated and another launched for a different site—with the same IP address and page name as your health-check page name (specified in your HEALTH_CHECK_URI RightScript input)—HAProxy could consider the server to be running and part of the load-balancer pool even though it is someone else's, and direct traffic to it.
Answer
Follow the steps below to set up a Health Check Page for HAProxy for your application (Tomcat, Rails, PHP).
When following the below examples, substitute occurrences of <######> or ###### with your own unique, random numeric string.
Warning: When specifying a HEALTH_CHECK_URI RightScript input, remember to include the health-check file in your application bundle. For example, in the case of Apache Tomcat, if you set HEALTH_CHECK_URI to /health\_check378923.jsp
, remember to include health_check378923.jsp in your WAR file.
Set up a Health Check Page
Apache Tomcat
Create a file named health_check<######>.jsp in your application with the following contents.
Set your HEALTH_CHECK_URI script input to:
/health\_check_<######>_.jsp
Ruby on Rails/Mongrel
Create a file named mongrel_health_check.rb with the below contents, and add it to your server or repository.
Modify the last line in the above file so that the page can be uniquely identified with your application (e.g. change
mongrel-status_######_
tomongrel-status1234089
).Add the following to /etc/mongrel_cluster/mongrel_cluster.yml:
config\_script: _<PathToFile>_/mongrel\_health\_check.rbOr, alternatively, set your OPT_MONGREL_CONFIG_SCRIPT input to the path where you saved the above file. Be sure to specify the full path to the file from the base directory of your Rails application; e.g.lib/mongrel\_health\_check\_handler.rb.Set HEALTH_CHECK_URI to the value you specified at the end of the file above: /mongrel-status_<######>_
PHP
Create a file named health_check_<######>_.php in your application with the following contents.
Set OPT_HEALTH_CHECK_URI to: /health_check_<######>_.php
Verify Health Check Pages
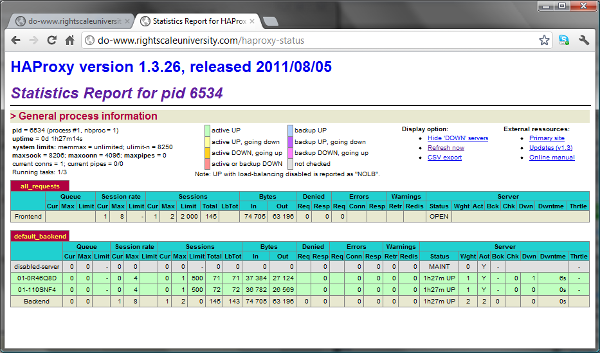
If your site's permissions allow it (and assuming that your script input OPT_LB_STATS_URI is set to haproxy-status) you can simply add /haproxy-status to your load-balancer hostname URL to display an HAProxy status report in a tabular HTML format:
Example: http://www.mysite.com/haproxy-status